Gynaecological examination
From puberty onwards, a woman will regularly consult a gynaecologist. This can be once, twice or three times a year for ‘routine’ check-ups, but also for advice on contraception, fertility, menopause, pregnancy, problems around menstruation, vaginal infections and sexuality.
Your visit to the gynaecologist starts with a conversation with the physician about any possible problems (medical history). This is followed, if necessary, by an external and/or internal examination of the genitals. To this end, you will be asked to take a seat in the gynaecological examination chair or on the examination table.
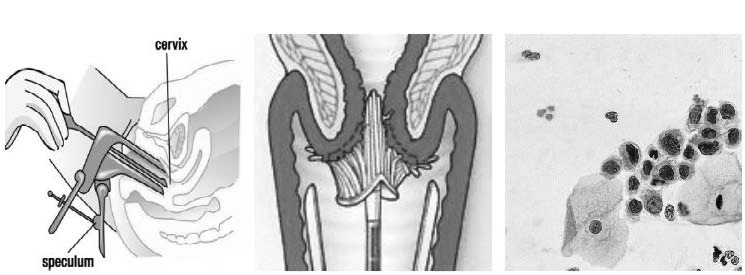
The examination usually consists of four parts:
Something wrong or unclear on this page? Report it.


