Hepatitis, viral
Symptoms and causes
Symptoms and causesHepatitis A, B, C, D, E viruses, CMV (cytomegaly virus) and the Epstein-Barr virus (glandular fever) are well known. They can cause an acute condition that heals completely within a few weeks with the help of one's own immune system.
Sometimes, they evolve into a chronic inflammation that no longer heals spontaneously. Because some of these inflammations, after decades, thoroughly disfigure the architecture of the liver through scar tissue (fibrosis), they can lead to liver cirrhosis, sometimes a life-threatening condition. That is why these conditions must be properly monitored and, where possible, treated with medication. Science has already enabled a number of victories against these diseases.
Hepatitis A
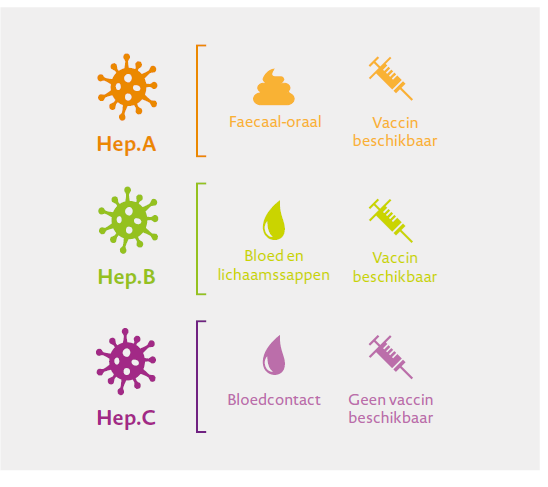
Hepatitis A is an acute form. The virus is usually transmitted by consuming food and water that is contaminated with the hepatitis A virus or through oral-anal sexual contact. It mainly occurs in children, but can also occur in adults. Children often become less sick than adults. The disease breaks out two to seven weeks after infection. Symptoms include that you feel tired, lack of appetite, nausea and sometimes jaundice. The enlarged liver causes abdominal pain. The time a person feels sick varies between a few weeks and three months or longer.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Infection takes place through saliva, blood or blood products (through syringes) and unsafe sexual contact (without a condom). This form can also be transferred from a mother to an unborn baby. In 90% of people, hepatitis B heals on its own, but in 10% of cases it becomes chronic. If the virus is no longer in a person's blood, it cannot be transmitted anymore. Most people who have hepatitis B do not have any symptoms.
Hepatitis C
This type is spread through blood and blood products (which are currently tested for the virus) or by a mother to a child during birth. The hepatitis C virus can be present in the body for years without any symptoms. In 80% of the cases, hepatitis C leads to chronic hepatitis. Hepatitis C is widely seen among injecting drug users. Infection by blood or blood products (during a blood transfusion) no longer occurs in Belgium. In non-Western countries, however, this is still a real danger.
Hepatitis D
You can only get the hepatitis D virus if you are also infected with the hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis D exacerbates the symptoms of hepatitis B. Infection occurs through blood or blood products, unsafe sexual contact or from mother to child during birth. You can contract the hepatitis D virus at the same time as the hepatitis B virus, or later, if you already have the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is similar to hepatitis A. In healthy people, the hepatitis E infection goes away on its own. People who have reduced immunity can develop a chronic hepatitis E infection.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis and treatmentThe treatment of chronic hepatitis B and C with antiviral drugs in particular is becoming increasingly successful. When medications no longer help and liver function becomes too weak after a long illness, the sick liver can be replaced with a transplant liver. Liver transplants are only performed at the university centres in Belgium.
Treatment centres and specialisations
Treatment centres and specialisations
Latest publication date: 02/08/2024
Supervising author: Dr Monsaert Els
Something wrong or unclear on this page? Report it.
Supervising author: Dr Monsaert Els




