Coronary CT angiography
What is it?
What is it?Coronary CT angiography is a very recent technique used to test the heart and to detect any constrictions in the coronary arteries. Using a simple intravenous injection of contrast agent and a high-quality scanner, images are taken of the coronary arteries, as well as of the other structures such as the heart muscle and heart valves.
Using the scanner, the functionality of some stents and of shunts can be evaluated. Your cardiologists is the appropriate person to evaluate whether you are a candidate for this test technique.
What is the process?
What is the process?Preparation
You must be fasting for this test. That means at least two hours for clear fluids (only water, tea and coffee), at least six hours for a light meal and dairy products and at least eight hours for a regular meal.
You may take your regular medications, unless this medication can cause an increased heart rate. Your cardiologist will give you specific medication guidelines to follow.
In order to guarantee an optimal image quality, you must have your heartbeat between 50 and 60 beats per minute. We sometimes give medication (beta blockers) to slow your heart rate. The medication can be given by the cardiologist or at the Radiology Department.
The test will not be performed if:
- you are pregnant
- are extremely obese
- have severe renal failure
The advantages and disadvantages must be weighed in the following circumstances:
- If you have an allergy or intolerance to contrast agent
- If you have an irregular heartbeat
- If you have problems holding your breath for a few seconds
Diabetic patients should consult their cardiologist beforehand regarding medications.
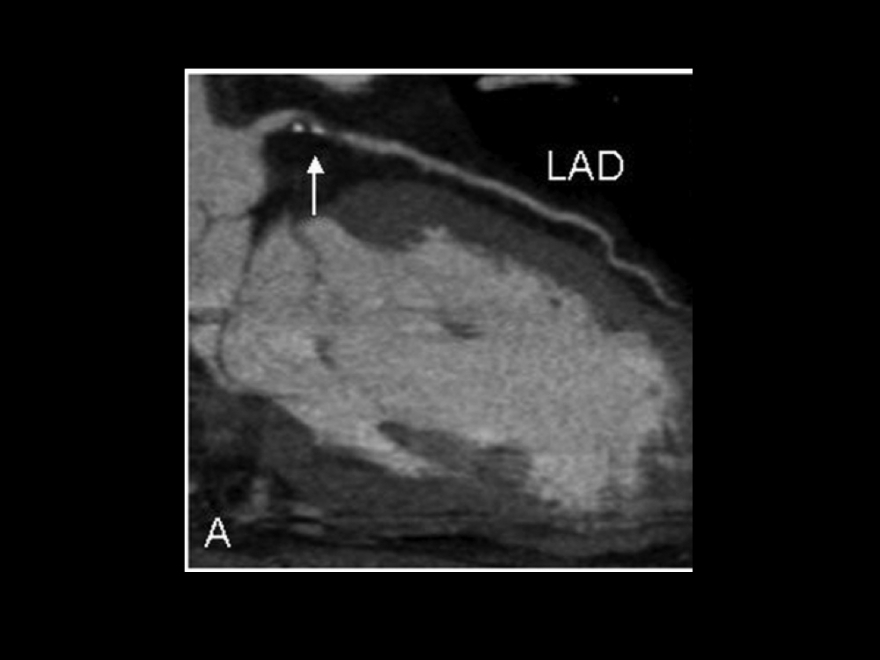
Test
The sleep study takes place at the Radiology Department. Immediately prior to the test, electrodes will be attached to your chest to monitor your heart rate, similar to a classic electrocardiogram. Your blood pressure will also be monitored during the test.
An IV will be placed in your arm in order to administer the contrast agent. Afterwards, a classic CT scan will be performed, during which you will be asked at regular intervals to hold your breath for a few seconds. You will be in the scan room for approximately ten minutes.
Aftercare
If there are no side effects from the contrast agent or from the beta blockers, you may leave the department immediately after the test.
What are the risks?
What are the risks?Allergic reactions to the contrast may occur in very rare cases. The radiology staff is trained to recognise this reaction, in the rare event that it does occur. The Radiology Department has the necessary medication and devices necessary to counteract this side effect. If patients with chronic renal failure need this test, the physician may decide to do it at the hospital. This is so the patient can receive sufficient fluids to protect the kidneys.
Results
ResultsYou will not yet have the results when you leave the test room. The images need to be interpreted by the radiologist, who will then prepare a report and send it to the requesting cardiologist. This may take a few days. Your cardiologist will have told you beforehand how the results will be communicated to you: in a letter from your GP, by telephone or during a consultation.
Centres and specialist areas
Centres and specialist areas
Something wrong or unclear on this page? Report it.
Latest publication date: 07/08/2024
Supervising author: Dr. Provenier Frank





